E-Mail | Security setup DKIM
These days security officers are struggling securing the e-mail and prevent that snooping or MTM (Man in The Middle) attacks. There are various protocols available to secure the e-mail.
You can use SPF, DKIM or DMARC for securing the e-mail traffic over the internet. The protect against phishing, spam, viruses and other malware by securing the sender (e-mail address/domain), the sending host (mail system) and the authenticity (contents) of an e-mail message. Enabling the standards involves adding records to the domain name’s DNS details. Also is a MTA-STS a possibility to help. Let’s deep dive in DKIM.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an email authentication method that allows email senders to verify that their messages are legitimate and have not been tampered with during transmission. DKIM uses public key cryptography to add a digital signature to each outgoing email message, which can be verified by the recipient’s email server to confirm that the message was sent by the legitimate sender and has not been modified in transit.
Why?
There are several reasons why you should use DKIM for your email authentication:
- Improved email deliverability: DKIM can help improve your email deliverability rates by reducing the likelihood of your messages being marked as spam or rejected by email servers. By adding a digital signature to your outgoing messages, you can provide email servers with a way to verify that your messages are legitimate and have not been tampered with, which can increase their trust in your messages and reduce the likelihood of them being blocked or marked as spam.
- Protection against email spoofing: DKIM provides a way to verify that the sender of an email message is legitimate and has not been forged or spoofed. By adding a digital signature to your messages, you can help protect against phishing attacks and other types of email fraud, which often use forged sender addresses to trick recipients into disclosing sensitive information or downloading malware.
- Brand protection: DKIM can help protect your brand’s reputation by ensuring that your messages are sent from legitimate sources and have not been tampered with. This can help build trust with your customers and improve their perception of your brand.
- Compliance with email authentication standards: Many email services and organizations require DKIM authentication as part of their email authentication standards. By implementing DKIM, you can ensure that your messages meet these requirements and are accepted by the recipient’s email server.
Overall, DKIM is an important tool for email authentication and can provide several benefits for your email marketing and communication efforts. By implementing DKIM, you can improve your email deliverability, protect against email fraud, and build trust with your customers.
How does DKIM work?
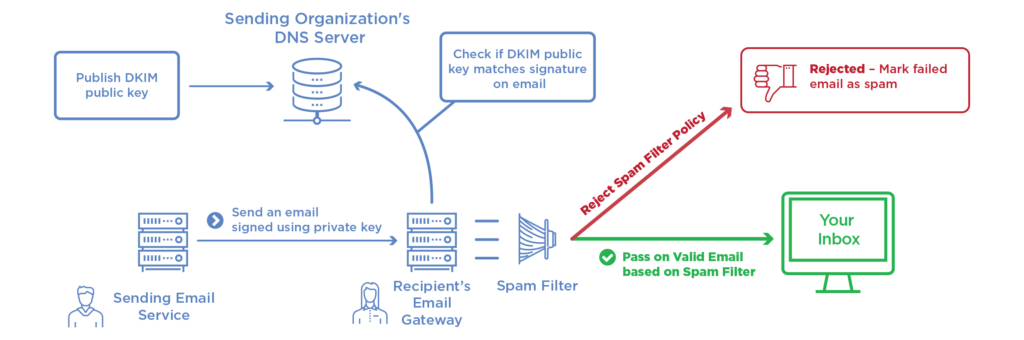
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) works by using public key cryptography to add a digital signature to each outgoing email message, which can be verified by the recipient’s email server to confirm that the message was sent by the legitimate sender and has not been modified in transit. Here’s how it works:
- Sender generates a public and private key pair: The sender’s email server generates a public and private key pair, with the private key kept secure on the sender’s email server.
- Sender publishes the public key: The sender publishes the public key in their domain’s DNS record. This allows recipient email servers to retrieve the public key to verify the digital signature on incoming email messages.
- Sender signs outgoing messages: When an email message is sent, the sender’s email server generates a unique digital signature for the message by applying a mathematical algorithm to the message’s content and the sender’s private key. The resulting signature is added to the message’s header as a DKIM signature.
- Recipient verifies the signature: When the recipient’s email server receives the message, it retrieves the public key from the sender’s DNS record and uses it to decrypt the signature. If the signature is valid, the recipient’s email server knows that the message was sent by the legitimate sender and has not been modified in transit.
DKIM is an effective way to combat email spoofing and phishing attacks, which often use forged sender addresses to trick recipients into disclosing sensitive information or downloading malware. By adding a digital signature to outgoing messages, email senders can provide recipients with a way to verify that the message is legitimate and has not been tampered with. DKIM also provides a way for email senders to build trust with email recipients and improve their email deliverability rates by reducing the likelihood of their messages being marked as spam or rejected by email servers.
Setup DKIM
To set up DKIM for your domain, you will need to follow these general steps:
- Generate a DKIM key pair: First, you will need to generate a DKIM key pair, which consists of a public key and a private key. You can generate a key pair using a DKIM generator tool or your email service provider’s DKIM setup process.
- Publish your DKIM public key in your domain’s DNS record: Once you have generated your DKIM key pair, you will need to publish the public key in your domain’s DNS record as a TXT record. The exact steps for doing this will depend on your domain registrar or DNS host, but typically involve logging into your DNS management console and creating a new TXT record that includes your DKIM public key.
- Configure your email service provider to sign outgoing email messages: You will need to configure your email service provider to use your private DKIM key to sign outgoing email messages. The exact steps for doing this will depend on your email service provider, but typically involve adding your private key to your email service provider’s DKIM configuration settings.
- Test your DKIM setup: Once you have published your DKIM public key and configured your email service provider to sign outgoing messages, you should test your DKIM setup to ensure that it is working correctly. You can do this using a DKIM testing tool or by sending a test email message and verifying that the DKIM signature is present and valid.
It’s important to note that the exact steps for setting up DKIM may vary depending on your specific email service provider, domain registrar, and DNS host.
DKIM-Signature: v=1; a=rsa-sha256; c=relaxed/relaxed; d=gettothe.cloud;
s=jan2018; t=1522244622;
bh=ZU6ml9h0D+T6Tzjq/L/QN8q3JqV7SBRaPaxuV7e8Nx4=;
h=From:To:Subject:Date:Message-ID:MIME-Version:Content-Type;
b=ctj5Q5D5l+9t33GBJtA5gPS/lwqdUNcF+IjZaefFztOhJWZI+q3Yn2yKjJrukdE+I
0eNSbNgknO5j+G5KW5PQ9bId5aMz7dG+oe/W8mCgSy1M35BjZNFbFZ/8vl/LY0cJ+0
rO/F24z25R1wNfR0nU6dDeL6hF8s7sU6vvyT6MhE=This DKIM signature includes the following elements:
- “v=1” indicates the version of DKIM being used.
- “a=rsa-sha256” specifies the algorithm used to sign the message.
- “c=relaxed/relaxed” specifies the canonicalization algorithm used for the header and body of the message.
- “d=gettothe.cloud” specifies the domain name that the signature is associated with.
- “s=jan2018” specifies the selector that identifies the public key used to verify the signature.
- “t=1522244622” specifies the time the message was signed.
- “bh=ZU6ml9h0D+T6Tzjq/L/QN8q3JqV7SBRaPaxuV7e8Nx4=” is the body hash of the message, which is calculated using the algorithm specified in the “a” tag.
- “h=From:To:Subject:Date:Message-ID:MIME-Version:Content-Type” specifies the header fields that were included in the signature.
- “b=ctj5Q5D5l+9t33GBJtA5gPS/lwqdUNcF+IjZaefFztOhJWZI+q3Yn2yKjJrukdE+I0eNSbNgknO5j+G5KW5PQ9bId5aMz7dG+oe/W8mCgSy1M35BjZNFbFZ/8vl/LY0cJ+0rO/F24z25R1wNfR0nU6dDeL6hF8s7sU6vvyT6MhE=” is the digital signature of the message, which is generated using the private key of the sending domain’s DKIM key pair.
This DKIM signature allows the receiving email server to verify that the message was not altered during transit and that it originated from the domain specified in the “d” tag.
How to test DKIM?
To test your DKIM setup, you can use one of several DKIM testing tools available online. Here’s a general process you can follow:
- Send a test email: Send a test email from your domain to a test email address that you control.
- Retrieve the email header: Once the test email has been received, retrieve the email header. The process for doing this will depend on your email client, but typically involves right-clicking on the email and selecting “View Source” or “View Original” to display the full email header.
- Copy the DKIM signature: Locate the DKIM signature in the email header and copy the entire signature, including the “DKIM-Signature” header field and its value.
- Use a DKIM testing tool: Go to a DKIM testing tool website, such as dkimcore.org/tools/, and paste the DKIM signature into the tool’s input field.
- Analyse the results: The DKIM testing tool will analyse the DKIM signature and provide a report on its validity. The report may include information on the public key used to sign the message, the signature algorithm, and any errors or warnings that were encountered.
If the DKIM testing tool reports that the signature is valid, then your DKIM setup is working correctly. If the tool reports errors or warnings, then you may need to troubleshoot your DKIM setup and make adjustments to your configuration.
It’s important to test your DKIM setup periodically to ensure that it continues to work correctly and to detect any issues that may arise.